插槽
| 分类 | Composition API(Vue3) | Options API(Vue3) | Options API(Vue2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 出口 | - | <slot> v3.0 | <slot> v2.0 |
| 声明 | defineSlots() v3.3 | slots v3.3 | - |
| 命名插槽 | - | 同上 | |
| 作用域插槽 | - | 同上 | |
| - | - | 同上 | |
| 读取 | useSlots() v3.0 | $slots v3.0 | $slots v2.0 |
| - | - | - | |
| 绑定 | - | v-slot v3.0 | v-slot v2.6 |
大纲
- 插槽
- 内容和出口
- 声明
- 读取
- 绑定
- Render Props
插槽内容和出口
<template>
<FancyButton>
Click me! <!-- slot content -->
</FancyButton>
<!-- FancyButton -->
<button class="fancy-btn">
<slot></slot> <!-- slot outlet -->
</button>
</template>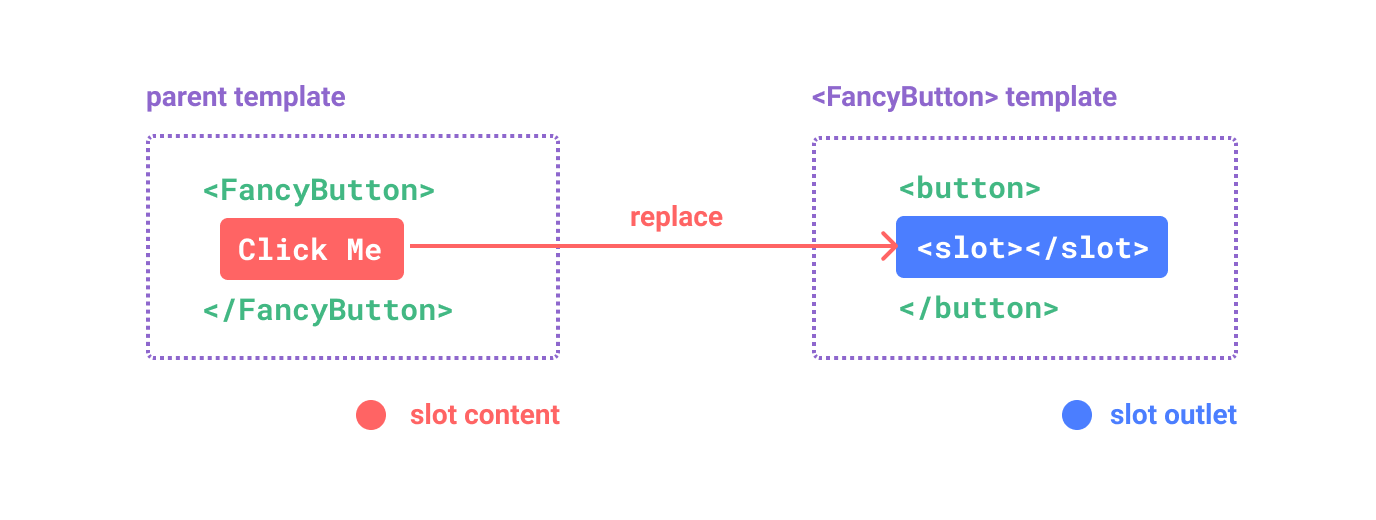
默认插槽及值
在某些情况下,为插槽指定回退(默认)内容很有用,仅在未提供任何内容时呈现。
<template>
<SubmitButton />
<!-- SubmitButton -->
<button type="submit">
<slot>
Submit <!-- fallback content -->
</slot>
</button>
</template>插槽声明
defineSlots()
defineSlots() 可用于向 IDE 提供类型提示,以进行 slot 名称和属性的类型检查。
defineSlots() 仅接受类型参数,不接受运行时参数。类型参数应为类型文字,其中属性 key 是槽名称,value 类型是槽函数。该函数的第一个参数是 slot 期望接收的 props,其类型将用于模板中的 slot props,返回类型目前是被忽略,可以是 any,但将来我们可能会利用它来检查插槽内容。
defineSlots() 还返回 slots 对象,该对象等效于在 setup 上下文中公开的 slots 对象或由 useSlots() 返回的对象。
<script setup lang="ts">
const slots = defineSlots<{
default(props: { msg: string }): any
}>()
</script>在 <script setup> 内使用 slots 和 attrs 应用相对较少,因为你可以直接通过 $slots 和 $attrs 在模板中访问它们。在极少数情况下,你确实需要它们,可分别使用 useSlots() 和 useAttrs() 帮助函数。
<script setup>
import { useSlots, useAttrs } from 'vue'
const slots = useSlots();
const attrs = useAttrs();
</script>useSlots() 和 useAttrs() 实际是运行时函数,它们返回和 setupContext.slots 和 setupContext.attrs 等效。它们也可以用于普通的组合式 API 函数。
slots
slots 选项是在 render 函数中以编程方式使用插槽时协助类型推断的选项。运行时的值不使用此选项。实际类型应该使用 SlotsType 类型帮助程序通过类型转换来声明:
import { SlotsType } from 'vue'
defineComponent({
slots: Object as SlotsType<{
default: { foo: string; bar: number }
item: { data: number }
}>,
setup(props, { slots }) {
expectType<
undefined | ((scope: { foo: string; bar: number }) => any)
>(slots.default)
expectType<undefined | ((scope: { data: number }) => any)>(
slots.item
)
}
})插槽读取
有时,希望根据是否存在插槽来渲染某些内容。可以将 $slots 数据与 v-if 结合起来实现这一点。
<template>
<div class="card">
<div v-if="$slots.header" class="card-header">
<slot name="header" />
</div>
<div v-if="$slots.default" class="card-content">
<slot />
</div>
<div v-if="$slots.footer" class="card-footer">
<slot name="footer" />
</div>
</div>
</template>插槽绑定
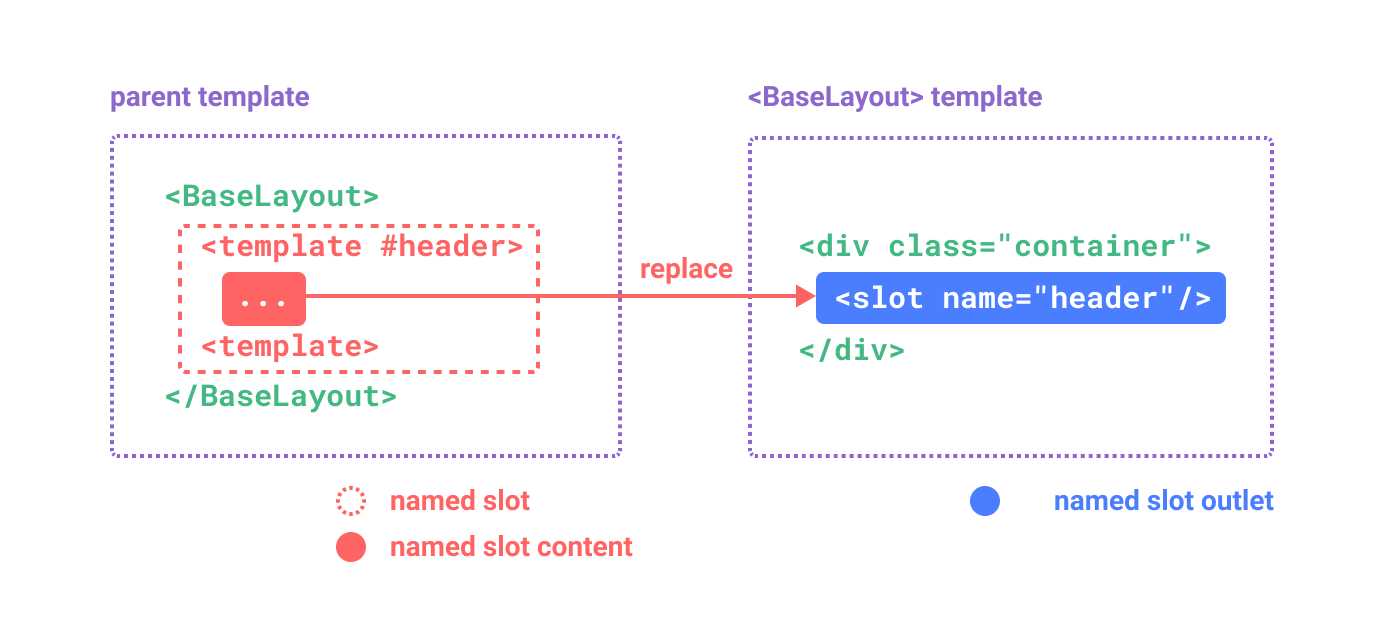
命名插槽
有时,在单个组件中具有多个插槽出口很有用。对于这种情况,<slot> 元素有一个特殊属性 name。该属性可用于为不同的插槽分配唯一ID,以便确定应呈现内容的位置:
没有 name 的出口 <slot> 隐式具有名称 “default”。
要传递命名插槽,我们需要使用带有 v-slot 指令的 <template> 元素。然后将插槽的名称作为参数传递给 v-slot。
<template>
<BaseLayout>
<template v-slot:header>
<!-- content for the header slot -->
</template>
</BaseLayout>
</template>v-slot 具有专用的简写形式 #,<template v-slot:header> 因此可以缩写为 <template #header>。可以将其视为 “在子组件的 ‘header’ 插槽中渲染此模板片段”。
当组件同时接受默认插槽和命名插槽时,所有顶级非 <template> 节点都将被隐式视为默认插槽的内容。
动态插槽
动态指令参数也适用于 v-slot,允许定义动态插槽名称:
<template>
<base-layout>
<template v-slot:[dynamicSlotName]>
...
</template>
<!-- with shorthand -->
<template #[dynamicSlotName]>
...
</template>
</base-layout>
</template>作用域插槽
插槽内容无权访问子组件中的 state。但是,某些情况下,如果插槽的内容可以使用父范围和子范围的数据,则可能会很有用。
如果将命名插槽与默认插槽混合使用,则需要为默认插槽使用显式标签。否则将导致编译错误。
<template>
<MyComponent>
<!-- Use explicit default slot -->
<template #default="{ message }">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
</template>
<template #footer>
<p>Here's some contact info</p>
</template>
</MyComponent>
<!-- <MyComponent> template -->
<div>
<slot :message="hello"></slot>
<slot name="footer" />
</div>
</template>